numpy ones & zeros & ones_like & zeros_like
numpy.ones(shape, dtype=None, order='C', *, like=None)
np.ones((5,),dtype = int)
array([1, 1, 1, 1, 1])
f = np.ones((2,3))
f
array([[1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1.]])
numpy.zeros(shape, dtype=float, order='C', *, like=None)
# 2행 4열
a = np.zeros((2,4), dtype = int)
a
array([[0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0]])
numpy.ones_like(a, dtype=None, order='K', subok=True, shape=None)
arr1 = np.array([[2,3,4],[5,6,7]])
ones_like_arr = np.ones_like(arr1)
print(ones_like_arr)
[[1 1 1] [1 1 1]]
ones_like 함수는 주어진 배열과 같은 shape과 dtype을 가지는 배열을 생성합니다. 주어진 배열과 동일한 모양으로 1로 채워진 배열을 만듭니다.
numpy.zeros_like(a, dtype=None, order='K', subok=True, shape=None)
arr2 = np.array([[2,3,4],[5,6,7]])
zeros_like_arr = np.zeros_like(arr1)
print(zeros_like_arr)
[[0 0 0] [0 0 0]]
대입 연산자와 copy 의 차이
- 대입 연산자는 깊은 복사, copy 연산자는 얕은 복사 ⇒ 메모리를 덜 차지함
대입 연산자
#대입연산자 (5를 100으로 바꾸기)
a = np.array([[1,2,3],[5,6,7]])
b = a
b[1][0] = 100
b
array([[ 1, 2, 3], [100, 6, 7]])
b[1,0]
100
copy 연산자
numpy.copy(a, order='K', subok=False)
#copy 연산자
a = np.array([[1,2,3],[5,6,7]])
b = np.array(a, copy = True)
b
array([[1, 2, 3], [5, 6, 7]])
a = np.array([[1,2,3],[5,6,7]])
b = a.copy()
b
array([[1, 2, 3], [5, 6, 7]])
a = np.array([[1,2,3],[5,6,7]])
b = np.copy(a)
b
array([[1, 2, 3], [5, 6, 7]])
numpy identity & numpy eye
numpy.identity(n, dtype=None, *, like=None)
대각선이 1로 채워지는 행렬
np.identity(4)
array([[1., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 1., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 1.]])
numpy.eye(N, M=None, k=0, dtype=<class 'float'>, order='C', *, like=None)
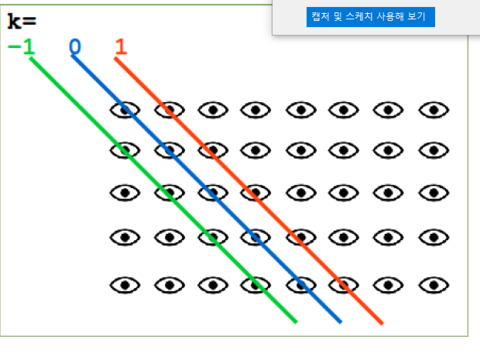
np.eye(5,8, k = 1, dtype = int)
array([[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0]])
DATA TYPE OBJECTS, DTYPE
import numpy as np
i16 = np.dtype(np.int16)
print(i16)
int16
lst = [ [3.4, 8.7, 9.9],
[1.1, -7.8, -0.7],
[4.1, 12.3, 4.8] ]
np.array(lst, dtype = i16)
array([[ 3, 8, 9],
[ 1, -7, 0],
[ 4, 12, 4]], dtype=int16)
STRUCTURED ARRAYS
- numpy.dtype
- class numpy.dytpe(dytpe, align = Fasle, copy = False[,metadata])
#np.dytpe('문자열', np.int)
dt = np.dtype([('density', np.int32)])
x = np.array([(393,), (337,), (256,)], dtype=dt)
x['density']
array([393, 337, 256])
#np.dytpe('문자열', np.int)
dt = np.dtype([('density', np.int32),('square', np.float32)])
x = np.array([(393,200), (337,300), (256,400)], dtype=dt)
array([200., 300., 400.], dtype=float32)
x['square']
ct = np.dtype([('country', np.string_), ('density','i4'),('area','i4'),('population', 'i4')])
c = np.array([
('Netherlands', 393, 41526, 16928800),
('Belgium', 337, 30510, 11007020),
('United Kingdom', 256, 243610, 62262000),
('Germany', 233, 357021, 81799600),
('Liechtenstein', 205, 160, 32842),
('Italy', 192, 301230, 59715625),
('Switzerland', 177, 41290, 7301994),
('Luxembourg', 173, 2586, 512000),
('France', 111, 547030, 63601002),
('Austria', 97, 83858, 8169929),
('Greece', 81, 131940, 11606813),
('Ireland', 65, 70280, 4581269),
('Sweden', 20, 449964, 9515744),
('Finland', 16, 338424, 5410233),
('Norway', 13, 385252, 5033675)],
dtype = ct
)
c
array([(b'', 393, 41526, 16928800), (b'', 337, 30510, 11007020),
(b'', 256, 243610, 62262000), (b'', 233, 357021, 81799600),
(b'', 205, 160, 32842), (b'', 192, 301230, 59715625),
(b'', 177, 41290, 7301994), (b'', 173, 2586, 512000),
(b'', 111, 547030, 63601002), (b'', 97, 83858, 8169929),
(b'', 81, 131940, 11606813), (b'', 65, 70280, 4581269),
(b'', 20, 449964, 9515744), (b'', 16, 338424, 5410233),
(b'', 13, 385252, 5033675)],
dtype=[('country', 'S'), ('density', '<i4'), ('area', '<i4'), ('population', '<i4')])
ct = np.dtype([('country', 'S20'), ('density','i4'),('area','i4'),('population', 'i4')])
c = np.array([
('Netherlands', 393, 41526, 16928800),
('Belgium', 337, 30510, 11007020),
('United Kingdom', 256, 243610, 62262000),
('Germany', 233, 357021, 81799600),
('Liechtenstein', 205, 160, 32842),
('Italy', 192, 301230, 59715625),
('Switzerland', 177, 41290, 7301994),
('Luxembourg', 173, 2586, 512000),
('France', 111, 547030, 63601002),
('Austria', 97, 83858, 8169929),
('Greece', 81, 131940, 11606813),
('Ireland', 65, 70280, 4581269),
('Sweden', 20, 449964, 9515744),
('Finland', 16, 338424, 5410233),
('Norway', 13, 385252, 5033675)],
dtype = ct
)
c
array([(b'Netherlands', 393, 41526, 16928800),
(b'Belgium', 337, 30510, 11007020),
(b'United Kingdom', 256, 243610, 62262000),
(b'Germany', 233, 357021, 81799600),
(b'Liechtenstein', 205, 160, 32842),
(b'Italy', 192, 301230, 59715625),
(b'Switzerland', 177, 41290, 7301994),
(b'Luxembourg', 173, 2586, 512000),
(b'France', 111, 547030, 63601002),
(b'Austria', 97, 83858, 8169929),
(b'Greece', 81, 131940, 11606813),
(b'Ireland', 65, 70280, 4581269),
(b'Sweden', 20, 449964, 9515744),
(b'Finland', 16, 338424, 5410233),
(b'Norway', 13, 385252, 5033675)],
dtype=[('country', 'S20'), ('density', '<i4'), ('area', '<i4'), ('population', '<i4')])
ct = np.dtype([('country', np.unicode_, 20), ('density','i4'),('area','i4'),('population', 'i4')])
c = np.array([
('Netherlands', 393, 41526, 16928800),
('Belgium', 337, 30510, 11007020),
('United Kingdom', 256, 243610, 62262000),
('Germany', 233, 357021, 81799600),
('Liechtenstein', 205, 160, 32842),
('Italy', 192, 301230, 59715625),
('Switzerland', 177, 41290, 7301994),
('Luxembourg', 173, 2586, 512000),
('France', 111, 547030, 63601002),
('Austria', 97, 83858, 8169929),
('Greece', 81, 131940, 11606813),
('Ireland', 65, 70280, 4581269),
('Sweden', 20, 449964, 9515744),
('Finland', 16, 338424, 5410233),
('Norway', 13, 385252, 5033675)],
dtype = ct
)
array([('Netherlands', 393, 41526, 16928800),
('Belgium', 337, 30510, 11007020),
('United Kingdom', 256, 243610, 62262000),
('Germany', 233, 357021, 81799600),
('Liechtenstein', 205, 160, 32842),
('Italy', 192, 301230, 59715625),
('Switzerland', 177, 41290, 7301994),
('Luxembourg', 173, 2586, 512000),
('France', 111, 547030, 63601002),
('Austria', 97, 83858, 8169929),
('Greece', 81, 131940, 11606813),
('Ireland', 65, 70280, 4581269),
('Sweden', 20, 449964, 9515744),
('Finland', 16, 338424, 5410233),
('Norway', 13, 385252, 5033675)],
dtype=[('country', '<U20'), ('density', '<i4'), ('area', '<i4'), ('population', '<i4')])
ct = np.dtype([('country', 'U20'), ('density','i4'),('area','i4'),('population', 'i4')])
c = np.array([
('Netherlands', 393, 41526, 16928800),
('Belgium', 337, 30510, 11007020),
('United Kingdom', 256, 243610, 62262000),
('Germany', 233, 357021, 81799600),
('Liechtenstein', 205, 160, 32842),
('Italy', 192, 301230, 59715625),
('Switzerland', 177, 41290, 7301994),
('Luxembourg', 173, 2586, 512000),
('France', 111, 547030, 63601002),
('Austria', 97, 83858, 8169929),
('Greece', 81, 131940, 11606813),
('Ireland', 65, 70280, 4581269),
('Sweden', 20, 449964, 9515744),
('Finland', 16, 338424, 5410233),
('Norway', 13, 385252, 5033675)],
dtype = ct
)
array([('Netherlands', 393, 41526, 16928800),
('Belgium', 337, 30510, 11007020),
('United Kingdom', 256, 243610, 62262000),
('Germany', 233, 357021, 81799600),
('Liechtenstein', 205, 160, 32842),
('Italy', 192, 301230, 59715625),
('Switzerland', 177, 41290, 7301994),
('Luxembourg', 173, 2586, 512000),
('France', 111, 547030, 63601002),
('Austria', 97, 83858, 8169929),
('Greece', 81, 131940, 11606813),
('Ireland', 65, 70280, 4581269),
('Sweden', 20, 449964, 9515744),
('Finland', 16, 338424, 5410233),
('Norway', 13, 385252, 5033675)],
dtype=[('country', '<U20'), ('density', '<i4'), ('area', '<i4'), ('population', '<i4')])
구조화된 배열의 입력 및 출력
numpy.savetxt
- numpy.savetxt(fname, X, fmt='%.18e', delimiter=' ', newline='\n', header='', footer='', comments='# ', encoding=None)
np.savetxt('population_table.csv',
c,
fmt="%s;%d;%d;%d",
delimiter = '',
comments = '#data',
encoding = 'utf-8'
)
numpy.genfromtxt
- numpy.genfromtxt(fname, dtype=<class 'float'>, comments='#', delimiter=None, skip_header=0, skip_footer=0, converters=None, missing_values=None, filling_values=None, usecols=None, names=None, excludelist=None, deletechars=" !#$%&'()*+, -./:;<=>?@[\\]^{|}~", replace_space='_', autostrip=False, case_sensitive=True, defaultfmt='f%i', unpack=None, usemask=False, loose=True, invalid_raise=True, max_rows=None, encoding='bytes', *, ndmin=0, like=None)
예제
import numpy as np
A = np.array([ [11, 12, 13], [21, 22, 23], [31, 32, 33] ])
B = np.ones((3,3))
A+B
array([[12., 13., 14.], [22., 23., 24.], [32., 33., 34.]])
A*B
array([[11., 12., 13.], [21., 22., 23.], [31., 32., 33.]])
A = np.array([ [11, 12, 13], [21, 22, 23], [31, 32, 33] ])
B = np.ones((3,3))*3
np.dot(A,B)
array([[108., 108., 108.], [198., 198., 198.], [288., 288., 288.]])
비교 연산
a = np.array([ [True, True], [False, False]])
b = np.array([ [True, False], [True, False]])
np.logical_or(a,b)
array([[ True, True],
[ True, False]])
np.logical_and(a,b)
array([[ True, False],
[False, False]])
np.logical_not(a,b)
array([[False, False],
[ True, True]])
np.logical_xor(a,b)
array([[ True, True],
[ True, True]])
'빅데이터 분석가 양성과정 > Python' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Matplotlib ( 1 ) (0) | 2024.07.09 |
|---|---|
| Numpy ( 3 ) (1) | 2024.07.09 |
| Numpy ( 1 ) (0) | 2024.07.09 |
| Web Crawling - 네이버 금융 환율정보 / 시 / 블로그 / 뉴스 (2) | 2024.07.09 |
| Web Crawling - 옷 쇼핑몰 (0) | 2024.07.09 |
numpy ones & zeros & ones_like & zeros_like
numpy.ones(shape, dtype=None, order='C', *, like=None)
np.ones((5,),dtype = int)
array([1, 1, 1, 1, 1])
f = np.ones((2,3))
f
array([[1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1.]])
numpy.zeros(shape, dtype=float, order='C', *, like=None)
# 2행 4열
a = np.zeros((2,4), dtype = int)
a
array([[0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0]])
numpy.ones_like(a, dtype=None, order='K', subok=True, shape=None)
arr1 = np.array([[2,3,4],[5,6,7]])
ones_like_arr = np.ones_like(arr1)
print(ones_like_arr)
[[1 1 1] [1 1 1]]
ones_like 함수는 주어진 배열과 같은 shape과 dtype을 가지는 배열을 생성합니다. 주어진 배열과 동일한 모양으로 1로 채워진 배열을 만듭니다.
numpy.zeros_like(a, dtype=None, order='K', subok=True, shape=None)
arr2 = np.array([[2,3,4],[5,6,7]])
zeros_like_arr = np.zeros_like(arr1)
print(zeros_like_arr)
[[0 0 0] [0 0 0]]
대입 연산자와 copy 의 차이
- 대입 연산자는 깊은 복사, copy 연산자는 얕은 복사 ⇒ 메모리를 덜 차지함
대입 연산자
#대입연산자 (5를 100으로 바꾸기)
a = np.array([[1,2,3],[5,6,7]])
b = a
b[1][0] = 100
b
array([[ 1, 2, 3], [100, 6, 7]])
b[1,0]
100
copy 연산자
numpy.copy(a, order='K', subok=False)
#copy 연산자
a = np.array([[1,2,3],[5,6,7]])
b = np.array(a, copy = True)
b
array([[1, 2, 3], [5, 6, 7]])
a = np.array([[1,2,3],[5,6,7]])
b = a.copy()
b
array([[1, 2, 3], [5, 6, 7]])
a = np.array([[1,2,3],[5,6,7]])
b = np.copy(a)
b
array([[1, 2, 3], [5, 6, 7]])
numpy identity & numpy eye
numpy.identity(n, dtype=None, *, like=None)
대각선이 1로 채워지는 행렬
np.identity(4)
array([[1., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 1., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 1.]])
numpy.eye(N, M=None, k=0, dtype=<class 'float'>, order='C', *, like=None)

np.eye(5,8, k = 1, dtype = int)
array([[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0]])
DATA TYPE OBJECTS, DTYPE
import numpy as np
i16 = np.dtype(np.int16)
print(i16)
int16
lst = [ [3.4, 8.7, 9.9],
[1.1, -7.8, -0.7],
[4.1, 12.3, 4.8] ]
np.array(lst, dtype = i16)
array([[ 3, 8, 9],
[ 1, -7, 0],
[ 4, 12, 4]], dtype=int16)
STRUCTURED ARRAYS
- numpy.dtype
- class numpy.dytpe(dytpe, align = Fasle, copy = False[,metadata])
#np.dytpe('문자열', np.int)
dt = np.dtype([('density', np.int32)])
x = np.array([(393,), (337,), (256,)], dtype=dt)
x['density']
array([393, 337, 256])
#np.dytpe('문자열', np.int)
dt = np.dtype([('density', np.int32),('square', np.float32)])
x = np.array([(393,200), (337,300), (256,400)], dtype=dt)
array([200., 300., 400.], dtype=float32)
x['square']
ct = np.dtype([('country', np.string_), ('density','i4'),('area','i4'),('population', 'i4')])
c = np.array([
('Netherlands', 393, 41526, 16928800),
('Belgium', 337, 30510, 11007020),
('United Kingdom', 256, 243610, 62262000),
('Germany', 233, 357021, 81799600),
('Liechtenstein', 205, 160, 32842),
('Italy', 192, 301230, 59715625),
('Switzerland', 177, 41290, 7301994),
('Luxembourg', 173, 2586, 512000),
('France', 111, 547030, 63601002),
('Austria', 97, 83858, 8169929),
('Greece', 81, 131940, 11606813),
('Ireland', 65, 70280, 4581269),
('Sweden', 20, 449964, 9515744),
('Finland', 16, 338424, 5410233),
('Norway', 13, 385252, 5033675)],
dtype = ct
)
c
array([(b'', 393, 41526, 16928800), (b'', 337, 30510, 11007020),
(b'', 256, 243610, 62262000), (b'', 233, 357021, 81799600),
(b'', 205, 160, 32842), (b'', 192, 301230, 59715625),
(b'', 177, 41290, 7301994), (b'', 173, 2586, 512000),
(b'', 111, 547030, 63601002), (b'', 97, 83858, 8169929),
(b'', 81, 131940, 11606813), (b'', 65, 70280, 4581269),
(b'', 20, 449964, 9515744), (b'', 16, 338424, 5410233),
(b'', 13, 385252, 5033675)],
dtype=[('country', 'S'), ('density', '<i4'), ('area', '<i4'), ('population', '<i4')])
ct = np.dtype([('country', 'S20'), ('density','i4'),('area','i4'),('population', 'i4')])
c = np.array([
('Netherlands', 393, 41526, 16928800),
('Belgium', 337, 30510, 11007020),
('United Kingdom', 256, 243610, 62262000),
('Germany', 233, 357021, 81799600),
('Liechtenstein', 205, 160, 32842),
('Italy', 192, 301230, 59715625),
('Switzerland', 177, 41290, 7301994),
('Luxembourg', 173, 2586, 512000),
('France', 111, 547030, 63601002),
('Austria', 97, 83858, 8169929),
('Greece', 81, 131940, 11606813),
('Ireland', 65, 70280, 4581269),
('Sweden', 20, 449964, 9515744),
('Finland', 16, 338424, 5410233),
('Norway', 13, 385252, 5033675)],
dtype = ct
)
c
array([(b'Netherlands', 393, 41526, 16928800),
(b'Belgium', 337, 30510, 11007020),
(b'United Kingdom', 256, 243610, 62262000),
(b'Germany', 233, 357021, 81799600),
(b'Liechtenstein', 205, 160, 32842),
(b'Italy', 192, 301230, 59715625),
(b'Switzerland', 177, 41290, 7301994),
(b'Luxembourg', 173, 2586, 512000),
(b'France', 111, 547030, 63601002),
(b'Austria', 97, 83858, 8169929),
(b'Greece', 81, 131940, 11606813),
(b'Ireland', 65, 70280, 4581269),
(b'Sweden', 20, 449964, 9515744),
(b'Finland', 16, 338424, 5410233),
(b'Norway', 13, 385252, 5033675)],
dtype=[('country', 'S20'), ('density', '<i4'), ('area', '<i4'), ('population', '<i4')])
ct = np.dtype([('country', np.unicode_, 20), ('density','i4'),('area','i4'),('population', 'i4')])
c = np.array([
('Netherlands', 393, 41526, 16928800),
('Belgium', 337, 30510, 11007020),
('United Kingdom', 256, 243610, 62262000),
('Germany', 233, 357021, 81799600),
('Liechtenstein', 205, 160, 32842),
('Italy', 192, 301230, 59715625),
('Switzerland', 177, 41290, 7301994),
('Luxembourg', 173, 2586, 512000),
('France', 111, 547030, 63601002),
('Austria', 97, 83858, 8169929),
('Greece', 81, 131940, 11606813),
('Ireland', 65, 70280, 4581269),
('Sweden', 20, 449964, 9515744),
('Finland', 16, 338424, 5410233),
('Norway', 13, 385252, 5033675)],
dtype = ct
)
array([('Netherlands', 393, 41526, 16928800),
('Belgium', 337, 30510, 11007020),
('United Kingdom', 256, 243610, 62262000),
('Germany', 233, 357021, 81799600),
('Liechtenstein', 205, 160, 32842),
('Italy', 192, 301230, 59715625),
('Switzerland', 177, 41290, 7301994),
('Luxembourg', 173, 2586, 512000),
('France', 111, 547030, 63601002),
('Austria', 97, 83858, 8169929),
('Greece', 81, 131940, 11606813),
('Ireland', 65, 70280, 4581269),
('Sweden', 20, 449964, 9515744),
('Finland', 16, 338424, 5410233),
('Norway', 13, 385252, 5033675)],
dtype=[('country', '<U20'), ('density', '<i4'), ('area', '<i4'), ('population', '<i4')])
ct = np.dtype([('country', 'U20'), ('density','i4'),('area','i4'),('population', 'i4')])
c = np.array([
('Netherlands', 393, 41526, 16928800),
('Belgium', 337, 30510, 11007020),
('United Kingdom', 256, 243610, 62262000),
('Germany', 233, 357021, 81799600),
('Liechtenstein', 205, 160, 32842),
('Italy', 192, 301230, 59715625),
('Switzerland', 177, 41290, 7301994),
('Luxembourg', 173, 2586, 512000),
('France', 111, 547030, 63601002),
('Austria', 97, 83858, 8169929),
('Greece', 81, 131940, 11606813),
('Ireland', 65, 70280, 4581269),
('Sweden', 20, 449964, 9515744),
('Finland', 16, 338424, 5410233),
('Norway', 13, 385252, 5033675)],
dtype = ct
)
array([('Netherlands', 393, 41526, 16928800),
('Belgium', 337, 30510, 11007020),
('United Kingdom', 256, 243610, 62262000),
('Germany', 233, 357021, 81799600),
('Liechtenstein', 205, 160, 32842),
('Italy', 192, 301230, 59715625),
('Switzerland', 177, 41290, 7301994),
('Luxembourg', 173, 2586, 512000),
('France', 111, 547030, 63601002),
('Austria', 97, 83858, 8169929),
('Greece', 81, 131940, 11606813),
('Ireland', 65, 70280, 4581269),
('Sweden', 20, 449964, 9515744),
('Finland', 16, 338424, 5410233),
('Norway', 13, 385252, 5033675)],
dtype=[('country', '<U20'), ('density', '<i4'), ('area', '<i4'), ('population', '<i4')])
구조화된 배열의 입력 및 출력
numpy.savetxt
- numpy.savetxt(fname, X, fmt='%.18e', delimiter=' ', newline='\n', header='', footer='', comments='# ', encoding=None)
np.savetxt('population_table.csv',
c,
fmt="%s;%d;%d;%d",
delimiter = '',
comments = '#data',
encoding = 'utf-8'
)

numpy.genfromtxt
- numpy.genfromtxt(fname, dtype=<class 'float'>, comments='#', delimiter=None, skip_header=0, skip_footer=0, converters=None, missing_values=None, filling_values=None, usecols=None, names=None, excludelist=None, deletechars=" !#$%&'()*+, -./:;<=>?@[\\]^{|}~", replace_space='_', autostrip=False, case_sensitive=True, defaultfmt='f%i', unpack=None, usemask=False, loose=True, invalid_raise=True, max_rows=None, encoding='bytes', *, ndmin=0, like=None)
예제
import numpy as np
A = np.array([ [11, 12, 13], [21, 22, 23], [31, 32, 33] ])
B = np.ones((3,3))
A+B
array([[12., 13., 14.], [22., 23., 24.], [32., 33., 34.]])
A*B
array([[11., 12., 13.], [21., 22., 23.], [31., 32., 33.]])
A = np.array([ [11, 12, 13], [21, 22, 23], [31, 32, 33] ])
B = np.ones((3,3))*3
np.dot(A,B)
array([[108., 108., 108.], [198., 198., 198.], [288., 288., 288.]])
비교 연산
a = np.array([ [True, True], [False, False]])
b = np.array([ [True, False], [True, False]])
np.logical_or(a,b)
array([[ True, True],
[ True, False]])
np.logical_and(a,b)
array([[ True, False],
[False, False]])
np.logical_not(a,b)
array([[False, False],
[ True, True]])
np.logical_xor(a,b)
array([[ True, True],
[ True, True]])
'빅데이터 분석가 양성과정 > Python' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Matplotlib ( 1 ) (0) | 2024.07.09 |
|---|---|
| Numpy ( 3 ) (1) | 2024.07.09 |
| Numpy ( 1 ) (0) | 2024.07.09 |
| Web Crawling - 네이버 금융 환율정보 / 시 / 블로그 / 뉴스 (2) | 2024.07.09 |
| Web Crawling - 옷 쇼핑몰 (0) | 2024.07.09 |
